You have probably noticed the presence of EDTA in the INCI list of some non-certified cosmetic health and beauty products. But what do you really know about this ingredient and why is it not authorized in organic cosmetics?
In this article, we will reveal everything you need to know about this cosmetic ingredient!
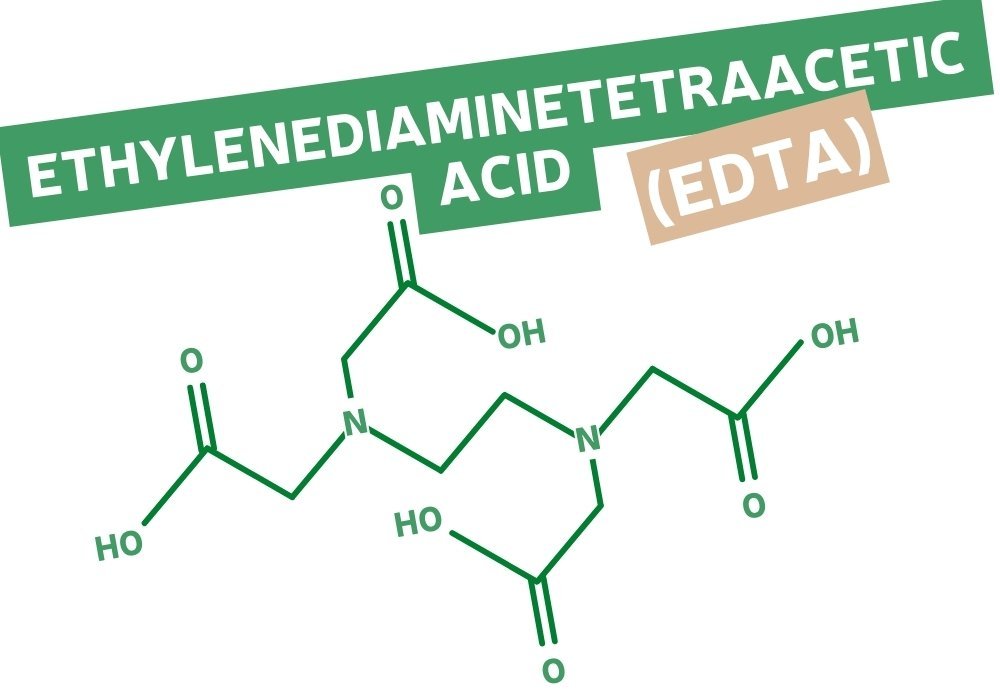
What is EDTA?
ETDA is a petrochemical that stands for Ethylene Diamine Tetra-Acetic Acid. It is known as a chelating agent, meaning it has the unique ability to capture and strongly bind to metal ions (calcium, magnesium, etc.) that are present in water or cosmetic formulations in order to improve their effectiveness and stability over time.
It can be used to:
- Increase the effectiveness of preservatives and antioxidants.
- Stabilize the color of certain formulations.
- Improve the foaming power of some cleansing products.
In which cosmetic products can EDTA be found?
Due to its various properties and high effectiveness, EDTA can be found in many non-organic cosmetic products such as Face creams, Shampoos, Conditioners, Hair masks, Shower gels, Soaps, Deodorants, Foundations...
How to identify EDTA in a cosmetic product?
EDTA is also used in the form of salts that have very similar properties. Identifying EDTA and its salts is easy! It can be found on the INCI list under various names that all include the abbreviation "EDTA."
Here are a few examples:
EDTA, Calcium Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, Disodium EDTA-Copper, Trisodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA
What are the issues surrounding EDTA in cosmetics?
Is EDTA dangerous for consumer health?
EDTA is deemed "sure" for cosmetic use in Europe. Due to its structure and physicochemical properties, EDTA cannot penetrate the skin.
Additionally, it is not considered a skin irritant nor an allergen. It use is considered safe at the low concentrations, which is usually the case when its incorporated in conventional cosmetic formulas.
Is EDTA dangerous for the environment?
Even though EDTA does not pose a major risk to consumer health, it is essential to stop using it if we want to preserve our environment.
Why? Because EDTA and its salts are not biodegradable. They can accumulate in aquatic ecosystems where they can bind to heavy metals and disrupt the biological balance of these environments. Once released into the environment, their fate and consequences remain uncertain.
Avoiding EDTA in your cosmetic products:
A non-biodegadable petrochemical...of course EDTA and its salts are not allowed in certified organic cosmetics ! Organic beauty brands know how to do away with EDTA. They replace it with other natural and more noble ingredients such as sodium gluconate (fermented glucose) or phytic acid (from cereals like wheat or rice), which are of natural origin, fully biodegradable, and non-toxic for us as well as the ecosystem.
To avoid EDTA, you can check the INCI list to ensure that the abbreviation "EDTA" does not appear among the ingredients.
Or even better, simply opt for certified organic cosmetics!